|
The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) came into being on Sunday, November 15th. This Asian trading block comprises 15 nations, including 10 members of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations and includes seven existing members of the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPATPP), established over four years ago. Following extensive negotiations through 2015 and 2016 the U.S. withdrew unilaterally from what was then the TPPA forerunner of the CPATPP in 2017. The policy of estanblishing separate bilateral agreements with China and Japan has been less beneficial than membership of the TPPA would have been.
|

China emerges as a winner with RCEP |
|
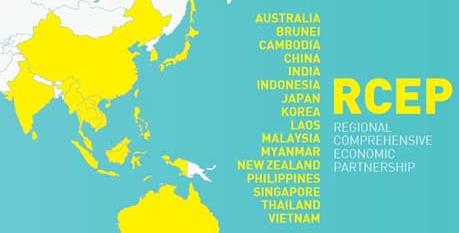
The RCEP is considered deficient in that both environmental and labor rules are poorly defined as are the sections on dispute settlement, competition and services. Despite shortcomings China appears to be a winner as it is now established as participant in an Asian trading group.
The incoming Administration will have to carefully evaluate future trade agreements but rejoining the CPATPP would appear to be the best option to counter the regional influence of China.
|